News
View the latest inspiring and positive news and information about what's going on in the PM and IT world.

DevOps is a dynamic and ever-improving set of practices that emphasizes collaboration and communication between software developers and other IT professionals.
All the people involved in developing software products and services and all the people dealing with delivering and managing those products and services do not all do the same things but needs some common skills in order to work together in a DevOps team.
The 'Upskilling: Enterprise DevOps Skills Report 2019' from DOI has identified the following “must-have” skills:
- Automation skills.
- Process skills.
- Soft skills.
DevOps Automation Skills
A DevOps professional is aiming to reduce waste and improve speed along the software development process, and automation is a key skill to succeed. A DevOps team member should also have knowledge around automation tools.
DevOps Process Skills
DevOps is Culture, so People and Process come first. This is the reason why Automation is important only if accompanied by working processes. DevOps professionals must have the capability to streamline processes to make them efficient.
The key process skills are:
- Software development life cycle.
- Understanding of process flow and analysis.
- Agile.
- Experience with test-driven deployment concepts and methods.
- System thinking.
DevOps Soft Skills
DevOps is not just software or IT, DevOps is Individuals as part of a Team. Individuals need to get engaged and motivated, this is the reason why soft skills have been considered as must-have skills.
The key soft skills are:
- Collaboration and cooperation.
- Problem-solving.
- Interpersonal skills.
- Sharing and knowledge transfer.
- Personal value commitment.
- Flexibility and adaptability.
A DevOps Leader must have these skills in order to lead people through a DevOps cultural transformation.
Discover the Skills That are Most Important to DevOps teams in 2019
Source: Based on the official report of the DevOps Institute, “2019 Upskilling: Enterprise DevOps Skills Report”.

A DevOps Leader is a transformational leader, leading people through a cultural transformation.
He/She focuses on creating a digital transformation, applying new techniques that have been proven by enterprise organizations. Organization’s profitability and productivity depend on the team capability to develop products, the good DevOps Leader enhances this capability.
The role of the DevOps Leader
DevOps Leader’s main responsibility is to build a great team and great technology. He/she is an enabler, a supporter, a leader that provides the foundation for a culture in which every member of a team learns every day and experiments every day.
This person is the professional responsibility to enable the necessary practices that correlate with high performance, and it also supports effective communication and collaboration between team members in pursuit of organizational goals.
The Responsibilities of the DevOps Leader
The DevOps Leader’s common responsibilities are:
- Oversee and guides all activities of the DevOps teams.
- Establish cultural norms.
- Promote improvement in the professional skills of the DevOps team.
- Support team experimentation.
- Promote, document, and implement technologies and processes that enhance developer productivity.
- Enhance communication/interaction between Developer and operations.
- Inspire and motivate.
The Competencies of the DevOps Leader
DevOps Leaders have typically 3 competencies:
- Inspirational Communication.
- This is the capability of a DevOps Leader to share an appealing vision that inspires and motivates the DevOps team to perform beyond expectations. The Leader encourages people to see the change as an opportunity.
- Intellectual stimulation.
- Capability to challenge a team to ask new questions, challenge assumptions, take risks and generate ideas.
- Personal recognition.
- Focus on the individual needs, acknowledge better performance and personally compliments for developments and achievements.
Latest DevOps Trends
The number of organizations which are using DevOps is increasing together with the spreading of frameworks and best practices like Agile and ITIL.
The key trends in DevOps and their impact on the profession of the DevOps Individuals are:
- “must-have” skills: automation skills, process, skills;
- “nice-to-have” skills: testing and enterprise/business architecture skills.
Source: 2019 upskilling: Enterprise DevOps Skills Report and 2017 state of the DevOps report.
Need a full DevOps Foundation Course?
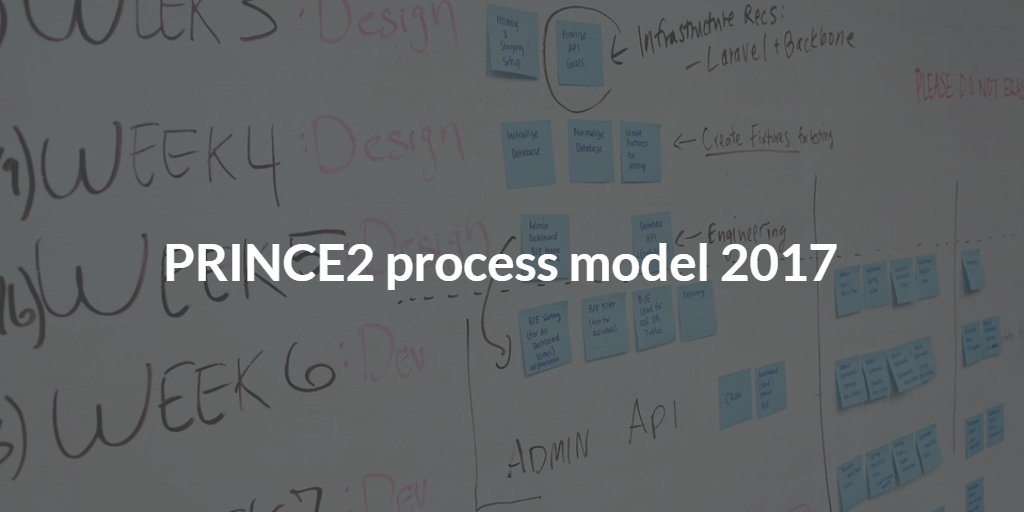
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environment) is a structured method for the effective and efficient management of projects. It is a generic, best-practice approach for the management of all types of projects and it has become the de facto standard for organising, managing and controlling projects globally.
The PRINCE2 process map is always one of the most downloaded documents from QRP International's download area: this graphic view of the PRINCE2 process involved within a project is a useful and relevant tool for:
- Project managers: anyone who is applying PRINCE2 at work would benefit from having a clear and graphic overview of the method.
- Course delegates: QRP International provides an A3 Process Map version as part of the training material during our courses, both classroom and distance learning.
PRINCE2 2017 Process Model PDF: a Renewed Process Map, updated to NEW Version
PRINCE2 is firmly established as the world’s most practised method for project management and is globally recognized for delivering successful projects. In July 2017 AXELOS released the first major update to PRINCE2 since 2009, with the 2017 version of the method: this brings along new PRINCE2 guidance and new Foundation and Practitioner examinations.
The 2017 update of PRINCE2 builds on the proven strength of PRINCE2, so the following key elements remain unchanged:
- 7 Processes forming the project management.
- 7 Principles forming the basis of good method of managing projects.
- 7 Themes knowledge areas which support specific key areas of project management
The purpose of the updated version is to better respond to current imperatives for flexibility and agility, and the new guidance wants to do so with a renewed focus on the importance of tailoring.
The PRINCE2 Process Flow Diagram is a graphical 'at a glance' representation of all the PRINCE2 processes and how they fit together and it shows all the processes involved in running a PRINCE2 project from start to finish.
The QRP International PRINCE2 Process map does not show only all the processes and how each stage integrates with the others but also what action needs to be taken for each process, which are the important products, documents or information to deliver during the stage for each management level (Team Manager, Project Manager, Project Board).
Looks complicated but it's not! This process map is a strong asset during your PRINCE2 Foundation and PRINCE2 Practitioner course and a helpful reference once back in the office as a project manager.
Our PRINCE2 Process Model is available for download in English, French and German: pick the language you prefer, don't miss this chance!
Download your English version!


Why DevOps Leadership?
Today’s organizations face a never-ending stream of internal and external forces that provide both opportunities and threats. The ability to adapt and innovate rapidly in this environment has become a core organizational competency. Successful DevOps adoption leads to the changes in systems development processes, technology, and culture that enable the organizational agility required to gain a competitive advantage. Leading people through a cultural transformation requires new skills, innovative thinking, and transformational leadership. Furthermore, the choice of leadership style has a direct influence on how members of the organization respond to the significant changes. However, organizational change initiatives have high failure. Bad planning, inadequate communications, unrealistic expectations, resistance to change, lack of preparation for change, low employee participation are among the main reasons why this occurs. The solution to these problems is how leaders act, how leaders engage others can significantly and positively influence employee response to change. Indeed, DevOps Leader has a great influence on the commitment of the followers to support organizational change. Personalized support, coaching, and encouragement: a DevOps Leader can be the added value the company needs to achieve a higher level of coordination and performance.
Why DevOps Leadership Courses?
Now an essential fact on DevOps Leadership should be considered: the behaviors of transformational leadership can be learned. Organizations can take proven measures to increase the probability of success for DevOps by investing in training, coaching and mentoring programs so that professionals can grow in their transformational leadership competence. Transformational leadership has been identified as a success factor for many DevOps adopters, personalized on many levels. Any organization has to develop the ability to think disruptively and to apply new approaches to get senior management endorsement. DevOps Leader course and associated certification focus on providing you transformational leadership skills. And remember: whatever you're a practitioner, a manager or part of a senior team, transformational leadership occurs at a different level: DevOps. While traditional leadership courses are about communication, collaboration and classical model, DevOps Leader Course focuses very specifically on leading DevOps users for creating a digital transformation through the application to new techniques and frameworks that have been proven by enterprises and experts of the fields.DevOps Leader Training & Certification
DevOps Leader is a 3 days classroom based course that highlights the human dynamics of cultural change and equips participants with practices, methods, and tools to engage people across the DevOps spectrum through the use of real-life scenarios and case studies. QRP International organizes accredited DevOps Leader courses all over Europe. Booking now one of our courses and become the DevOps Leader your company needs!| LEVEL | DURATION | LANGUAGE | DATE | CITY | AMOUNT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DevOps - Leader | 3 Days | French | 11-12-13 November 2019 | Geneva | 2 290 CHF |
| DevOps - Leader | 3 Days | German | 11-12-13 November 2019 | Zurich | 2 290 CHF |
| DevOps - Leader | 3 Days | English | 11-12-13 November 2019 | Zurich | 2 290 CHF |

What's PMO? And what does a PMO actually do? In this long interview, Tom Van Medegael, programme/project specialist, answers to the most common question about Project Manager Officer.
1. What's your current job title?
My official job title is "Methodologist" but (what's in a name ?) that's a very vague job title that doesn't really describe my current PMO activities.
2. What does a PMO actually do?
The work of a Project Manager Officer, as in my case, includes a different kind of activities and tasks as:
- standards & methods: selecting/customizing/developing methods and leading continuous improvement initiatives in the P3/PPM domain
- people and skills: presentations and training in the P3/PPM domain (PRINCE2 for Smals ICT, business cases, and ROI, estimation techniques, MSP for Smals…)
- programme/project setup and closure: facilitating workshops for setup (business case development etc) and closure (benefit reviews, lessons learned, etc) activities
- quality assurance: quality controls of the P3/PPM management products (mainly PIDs and Project Briefs) for projects realized by Smals ICT.
- performance monitoring: KPI's and benchmarking (productivity, time-to-market, quality, reuse levels…)
3. How did you end up into a project management career?
To be honest, I learned most about project management in my current job (PMO lead/project specialist). I didn't really have an idea during my university career what exactly project management was about (there were no PM courses at that time, we're talking about the eighties), I didn't have a predefined path in mind and just rolled into project management at some point by following a traditional career path: analyst, team manager and finally project manager. I'm glad I did, it's a fascinating job in an ever faster changing world where most change is realized by projects.
4. What's the biggest issue/change you see in your community at the moment?
The biggest issue I see in my environment, the Smals ICT project management community, at the moment is increasing complexity, due to interdependencies, accelerating change, quality expectations, cost reductions.
To clarify what I mean, I'll give you an example of increasing complexity in our business: until a couple of years ago, to realize a software development project, a project manager simply gathered requirements, then made an estimation (time/cost), asked approval and then put his development team to work. Nowadays, before asking approval, he has to consider GDPR impacts (EU regulation), solid IT security, usability and accessibility (EU regulation), reuse levels, interdependencies with other projects, make up a solid business case and so on. And all this has to be done without an extra budget and in much shorter delivery cycles. Without mentioning the increasing technological complexity in IT. I guess this reasoning applies to most of the project managers in IT and other industries too.
5. What are three things you’ve told yourself that you would like to learn in the next future to develop you as a professional?
Three of the competences I will further develop in the near future are Portfolio management, DevOps and Artificial intelligence.
Why I'm interested in DevOps and Artificial Intelligence? Well, DevOps is the next step at Smals ICT level moving from traditional (waterfall) to agile/lean approaches in realizing projects. Scrum has been used at Smals ICT for over ten years, DevOps is only at the starting point and as a PMO I feel the exigency to go in-depth with the method.
AI is the next big thing in IT (Smals ICT core business) which will affect also project management. Personally, I'm much interested to see how estimation techniques, for instance, will benefit from AI in the coming years. Estimation support being one of my core activities within the PMO.
Tom Van Medegael
Tom works for Smals ICT for society as PMO. As programme/project specialist he has achieved several Project Management Certificaitons (PMP, PRINCE2, AgilePM, MSP…).

ITIL Service Value Chain and contribution from PRINCE2
1. Plan “The purpose of the plan value chain activity is to ensure a shared understanding of the vision, current status, and improvement direction for all four dimensions and all products and services across the organization”. PRINCE2 can contribute to this activity by supporting strategic and tactical planning with the Product Based Planning approach: The products to be delivered must be identified before deciding what activities, dependencies, and resources are required to deliver products.” 2. Improve “The purpose of the improve value chain activity is to ensure continual improvement of products, services, and practices across all value chain activities and the four dimensions of service management”. You may need to improve your services, prioritize among several large and complex initiatives and you may need to evaluate the validity of each improvement initiative ongoing. PRINCE2 can drive you through the Continued business justification (the justifiable reason for starting a project that remains valid along with the project). This principle keeps the improvements projects focused on the goal. 3. Engage “The purpose of the engage value chain activity is to provide a good understanding of stakeholders needs, transparency, and continual engagement and good relationship with all stakeholders”. The organization theme helps to define an effective project management team structure, with agreed roles and responsibilities. Once you have defined the structure you can define an approach for the communication to engage the stakeholders, the business, the user and supplier. 4. Design and transition
“The purpose of the design and transition value chain activity is to ensure that products and services continually meet stakeholder expectations for quality, costs, and time to market”.
Design of a practice or service can be managed as a PRINCE2 project, PRINCE2 can contribute through its emphasis on the learning from experience. Lessons Learned can help avoid common pitfalls in designing, for example, a new service desk service.
5. Obtain/build
“The purpose of the obtain/build value chain activity is to ensure that service components are available when and where they are needed and meet agreed specifications”.
“Obtaining new resources as well as development and integration is usually performed as a project. Various project management techniques are applicable to this activity”
6. Deliver and support
“The purpose of the delivery and support value chain activity is to ensure that services are delivered and supported according to agreed specifications and stakeholders’ expectations”.
The design, transition, and handover to internal or external service consumers for operational management needs to be well planned and executed to ensure that business, as usual, is not compromised. The PRINCE2 project management practice to ensure the handover of the service for operations management needs is well planned and executed happens through the Benefits Management Approach, that defines not only how the project’s outcome will be achieved, but also how the project’s benefits will be realized, so that services are not only delivered but are also delivered according to the requirements and needs of the stakeholders.
With an understanding of both guidance, ITIL 4 and PRINCE2 together deliver a competitive advantage for an organization.
Source: ITIL Foundation, ITIL 4 Edition
4. Design and transition
“The purpose of the design and transition value chain activity is to ensure that products and services continually meet stakeholder expectations for quality, costs, and time to market”.
Design of a practice or service can be managed as a PRINCE2 project, PRINCE2 can contribute through its emphasis on the learning from experience. Lessons Learned can help avoid common pitfalls in designing, for example, a new service desk service.
5. Obtain/build
“The purpose of the obtain/build value chain activity is to ensure that service components are available when and where they are needed and meet agreed specifications”.
“Obtaining new resources as well as development and integration is usually performed as a project. Various project management techniques are applicable to this activity”
6. Deliver and support
“The purpose of the delivery and support value chain activity is to ensure that services are delivered and supported according to agreed specifications and stakeholders’ expectations”.
The design, transition, and handover to internal or external service consumers for operational management needs to be well planned and executed to ensure that business, as usual, is not compromised. The PRINCE2 project management practice to ensure the handover of the service for operations management needs is well planned and executed happens through the Benefits Management Approach, that defines not only how the project’s outcome will be achieved, but also how the project’s benefits will be realized, so that services are not only delivered but are also delivered according to the requirements and needs of the stakeholders.
With an understanding of both guidance, ITIL 4 and PRINCE2 together deliver a competitive advantage for an organization.
Source: ITIL Foundation, ITIL 4 Edition










